1984年开始,Case Gould就发表了一篇关于内毒素对细胞培养效应的综述1。本文缔一生物/缔一生物为您分析内毒素对体外细胞生长和功能的效应。
在这些效应中,包括刺激白细胞产生组织因子,激活小鼠巨噬细胞,抑制小鼠红细胞集落形成(极低浓度即有该效应,小于1ng/ml)。那之后,许多文章发表,报道内毒素的各种效应,部分见下面的表格。
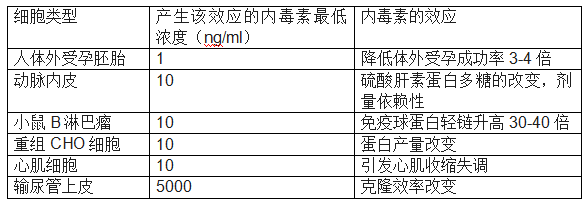
针对内毒素的刺激,免疫细胞的表现更为明显。巨噬细胞和单核细胞已知会产生和释放各种细胞因子,包括肿瘤坏死因子和白细胞介素等。Morris等人发现,马腹腔巨噬细胞暴露在低至0.5ng/ml内毒素中6个小时,也可引发显著的白细胞介素6产生2。Mattern显示,100ng内毒素刺激人T细胞增生,产生淋巴因子3。
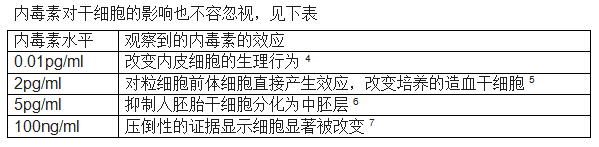
因此,选用尽可能低的内毒素的胎牛血清,显然是优上之选。
参考文献
1. Case Gould, et al. Endotoxin in Vertebrate Cell Culture: Its Measurement and Significance. In Uses and Standardization of Vertebrate Cell Lines,(Tissue Culture Association, Gaithersburg, MD,1984),125-136.
2. Morris, D.D.,et al. Endotoxin-induced production of interleukin6 by equine peritoneal macrophages In Vitro. Am.J.Vet.Res.1992,53:1298-1301
3. Mattern, T., et al. Endotoxin and lipid A stimulate proliferation of human T cells in the presence of autologous monocytes. J.Immunol.1994,153:2996-3004
4. Ronald E.Unger, et al. Human endothelial cell-based assay for endotoxin as sensitive as the conventional Limulus Amebocyte Lysate assay. Biomaterials. 2014,35(10):3180-3187
5. Rinehart J and Keville L. Effects of endotoxin on proliferation of human hematopoietic cell precursors. Cytotechnology (1997) 42:153-159.
6. Sivasubramaniyan K., et al. Endotoxin-induced silencing of mesoderm induction and functional differentiation: Role of HMGB1 in pluripotency and infection.Regenerative Medicine, 2008,3(1):23-31
7. Gorbet, M.B.; Sefton, M.V. Endotoxin: The uninvited guest. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6811–6817,
综上所述,您是不是已经对内毒素对体外细胞生长和功能的效应,有所了解。如果还有其他疑问,请咨询缔一生物/缔一生物资深专家:。